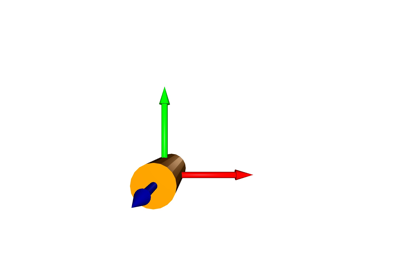
pytransform3d.visualizer.Cylinder#
- class pytransform3d.visualizer.Cylinder(length=2.0, radius=1.0, A2B=array([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 1.]]), resolution=20, split=4, c=None)[source]#
Bases:
ArtistCylinder.
A cylinder is the volume covered by a disk moving along a line segment.
- Parameters:
- lengthfloat, optional (default: 1)
Length of the cylinder.
- radiusfloat, optional (default: 1)
Radius of the cylinder.
- A2Barray-like, shape (4, 4)
Pose of the cylinder. The position corresponds to the center of the line segment and the z-axis to the direction of the line segment.
- resolutionint, optional (default: 20)
The circles will be split into resolution segments.
- splitint, optional (default: 4)
The height will be split into split segments
- carray-like, shape (3,), optional (default: None)
Color
- __init__(length=2.0, radius=1.0, A2B=array([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 1.]]), resolution=20, split=4, c=None)[source]#
Methods
__init__([length, radius, A2B, resolution, ...])add_artist(figure)Add artist to figure.
set_data(A2B)Update data.
Attributes
Expose geometries.
- property geometries#
Expose geometries.
- Returns:
- geometrieslist
List of geometries that can be added to the visualizer.
- add_artist(figure)#
Add artist to figure.
- Parameters:
- figureFigure
Figure to which the artist will be added.