pytransform3d.urdf.UrdfTransformManager#
- class pytransform3d.urdf.UrdfTransformManager(strict_check=True, check=True)[source]#
Bases:
TransformManagerTransformation manager that can load URDF files.
The Unified Robot Description Format (URDF) [1] is the most common format to describe kinematic and dynamic properties of robots [2]. This transformation manager allows to set the joint configurations of a robot loaded from a URDF file and provides an interface to its geometric and visual representation.
Warning
Note that this module requires the Python package lxml.
Note
Joint angles must be given in radians.
- Parameters:
- strict_checkbool, optional (default: True)
Raise a ValueError if the transformation matrix is not numerically close enough to a real transformation matrix. Otherwise we print a warning.
- checkbool, optional (default: True)
Check if transformation matrices are valid and requested nodes exist, which might significantly slow down some operations.
References
[1]ROS Wiki: urdf, http://wiki.ros.org/urdf
[2]Tola, D., Corke, P. (2023). Understanding URDF: A Dataset and Analysis. In IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 9(5), pp. 4479-4486, doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3381482. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.00514
Methods
__init__([strict_check, check])add_joint(joint_name, from_frame, to_frame, ...)Add joint.
add_transform(from_frame, to_frame, A2B)Register a transformation.
Check consistency of the known transformations.
Get number of connected components.
from_dict(tm_dict)Create transform manager from dict.
get_joint_limits(joint_name)Get limits of a joint.
get_transform(from_frame, to_frame)Request a transformation.
has_frame(frame)Check if frame has been registered.
load_urdf(urdf_xml[, mesh_path, package_dir])Load URDF file into transformation manager.
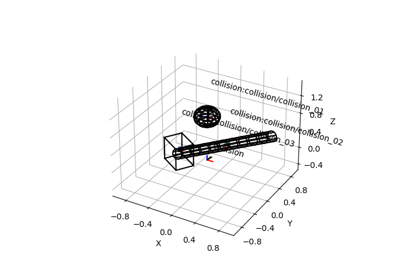
plot_collision_objects(frame[, ax, ax_s, ...])Plot all collision objects in a given reference frame.
plot_connections_in(frame[, ax, ax_s, whitelist])Plot direct frame connections in a given reference frame.
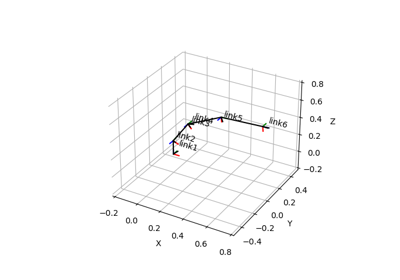
plot_frames_in(frame[, ax, s, ax_s, ...])Plot all frames in a given reference frame.
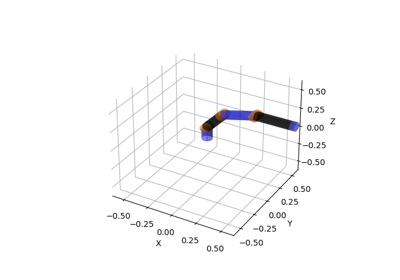
plot_visuals(frame[, ax, ax_s, wireframe, ...])Plot all visuals in a given reference frame.
remove_frame(frame)Remove a frame (node) from the graph.
remove_transform(from_frame, to_frame)Remove a transformation.
set_joint(joint_name, value)Set joint position.
set_transform_manager_state(tm_dict)Set state of transform manager from dict.
to_dict()Convert the transform manager to a dict that is serializable.
write_png(filename[, prog])Create PNG from dot graph of the transformations.
Attributes
Rigid transformations between nodes.
- add_joint(joint_name, from_frame, to_frame, child2parent, axis, limits=(-inf, inf), joint_type='revolute')[source]#
Add joint.
- Parameters:
- joint_namestr
Name of the joint
- from_frameHashable
Child link of the joint
- to_frameHashable
Parent link of the joint
- child2parentarray-like, shape (4, 4)
Transformation from child to parent
- axisarray-like, shape (3,)
Rotation axis of the joint (defined in the child frame)
- limitspair of float, optional (default: (-inf, inf))
Lower and upper joint angle limit
- joint_typestr, optional (default: ‘revolute’)
Joint type: revolute, prismatic, or fixed (continuous is the same as revolute)
- set_joint(joint_name, value)[source]#
Set joint position.
Note that joint values are clipped to their limits.
- Parameters:
- joint_namestr
Name of the joint
- valuefloat
Joint angle in radians in case of revolute joints or position in case of prismatic joint.
- Raises:
- KeyError
If joint_name is unknown
- get_joint_limits(joint_name)[source]#
Get limits of a joint.
- Parameters:
- joint_namestr
Name of the joint
- Returns:
- limitspair of float
Lower and upper joint angle limit
- Raises:
- KeyError
If joint_name is unknown
- load_urdf(urdf_xml, mesh_path=None, package_dir=None)[source]#
Load URDF file into transformation manager.
- Parameters:
- urdf_xmlstr
Robot definition in URDF
- mesh_pathstr, optional (default: None)
Path in which we search for meshes that are defined in the URDF. Meshes will be ignored if it is set to None and no ‘package_dir’ is given.
- package_dirstr, optional (default: None)
Some URDFs start file names with ‘package://’ to refer to the ROS package in which these files (textures, meshes) are located. This variable defines to which path this prefix will be resolved.
- plot_visuals(frame, ax=None, ax_s=1, wireframe=False, convex_hull_of_mesh=True, alpha=0.3)[source]#
Plot all visuals in a given reference frame.
Visuals can be boxes, spheres, cylinders, or meshes. Note that visuals that cannot be connected to the reference frame are omitted.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Reference frame
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- wireframebool, optional (default: False)
Plot wireframe (surface otherwise)
- convex_hull_of_meshbool, optional (default: True)
Displays convex hull of meshes instead of the original mesh. This makes plotting a lot faster with complex meshes.
- alphafloat, optional (default: 0.3)
Alpha value of the surface / wireframe that will be plotted
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
- plot_collision_objects(frame, ax=None, ax_s=1, wireframe=True, convex_hull_of_mesh=True, alpha=1.0)[source]#
Plot all collision objects in a given reference frame.
Collision objects can be boxes, spheres, cylinders, or meshes. Note that collision objects that cannot be connected to the reference frame are omitted.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Reference frame
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- wireframebool, optional (default: True)
Plot wireframe (surface otherwise)
- convex_hull_of_meshbool, optional (default: True)
Displays convex hull of meshes instead of the original mesh. This makes plotting a lot faster with complex meshes.
- alphafloat, optional (default: 1)
Alpha value of the surface / wireframe that will be plotted
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
- add_transform(from_frame, to_frame, A2B)#
Register a transformation.
- Parameters:
- from_frameHashable
Name of the frame for which the transformation is added in the to_frame coordinate system
- to_frameHashable
Name of the frame in which the transformation is defined
- A2BAny
Transformation from ‘from_frame’ to ‘to_frame’
- Returns:
- selfTransformManager
This object for chaining
- check_consistency()#
Check consistency of the known transformations.
The computational cost of this operation is very high.
- Returns:
- consistentbool
Is the graph consistent, i.e., if there are two ways of computing A2B, do they give almost identical results?
- connected_components()#
Get number of connected components.
If the number is larger than 1 there will be frames without connections.
- Returns:
- n_connected_componentsint
Number of connected components.
- static from_dict(tm_dict)#
Create transform manager from dict.
- Parameters:
- tm_dictdict
Serializable dict.
- Returns:
- tmTransformManager
Deserialized transform manager.
- get_transform(from_frame, to_frame)#
Request a transformation.
- Parameters:
- from_frameHashable
Name of the frame for which the transformation is requested in the to_frame coordinate system
- to_frameHashable
Name of the frame in which the transformation is defined
- Returns:
- A2BAny
Transformation from ‘from_frame’ to ‘to_frame’
- Raises:
- KeyError
If one of the frames is unknown or there is no connection between them
- has_frame(frame)#
Check if frame has been registered.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Frame name
- Returns:
- has_framebool
Frame is registered
- plot_connections_in(frame, ax=None, ax_s=1, whitelist=None, **kwargs)#
Plot direct frame connections in a given reference frame.
A line between each pair of frames for which a direct transformation is known will be plotted. Direct means that either A2B or B2A has been added to the transformation manager.
Note that frames that cannot be connected to the reference frame are omitted.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Reference frame
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- whitelistlist, optional (default: None)
Both frames of a connection must be in the whitelist to plot the connection
- kwargsdict, optional (default: {})
Additional arguments for the plotting functions, e.g. alpha
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
- Raises:
- KeyError
If the frame is unknown
- plot_frames_in(frame, ax=None, s=1.0, ax_s=1, show_name=True, whitelist=None, **kwargs)#
Plot all frames in a given reference frame.
Note that frames that cannot be connected to the reference frame are omitted.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Reference frame
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the frame that will be drawn
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- show_namebool, optional (default: True)
Print node names
- whitelistlist, optional (default: None)
Frames that must be plotted
- kwargsdict, optional (default: {})
Additional arguments for the plotting functions, e.g. alpha
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
- Raises:
- KeyError
If the frame is unknown
- remove_frame(frame)#
Remove a frame (node) from the graph.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
The frame to remove.
- Returns:
- selfTransformManager
This object for chaining.
- remove_transform(from_frame, to_frame)#
Remove a transformation.
Nothing happens if there is no such transformation.
- Parameters:
- from_frameHashable
Name of the frame for which the transformation is added in the to_frame coordinate system
- to_frameHashable
Name of the frame in which the transformation is defined
- Returns:
- selfTransformManager
This object for chaining
- set_transform_manager_state(tm_dict)#
Set state of transform manager from dict.
- Parameters:
- tm_dictdict
Serializable dict.
- to_dict()#
Convert the transform manager to a dict that is serializable.
- Returns:
- tm_dictdict
Serializable dict.
- property transforms#
Rigid transformations between nodes.
- write_png(filename, prog=None)#
Create PNG from dot graph of the transformations.
Warning
Note that this method requires the Python package pydot and an existing installation of graphviz on your system.
- Parameters:
- filenamestr
Name of the output file. Should end with ‘.png’.
- progstr, optional (default: dot)
Name of GraphViz executable that can be found in the $PATH or absolute path to GraphViz executable. Possible options are, for example, ‘dot’, ‘twopi’, ‘neato’, ‘circo’, ‘fdp’, ‘sfdp’.
- Raises:
- ImportError
If pydot is not available