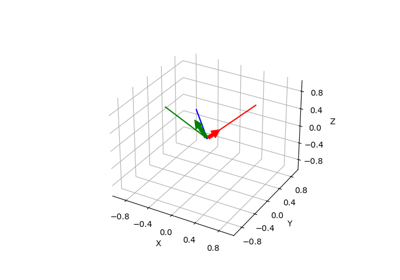
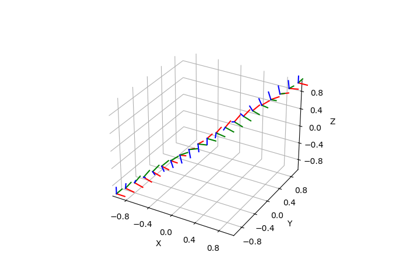
pytransform3d.rotations.plot_basis#
- pytransform3d.rotations.plot_basis(ax=None, R=None, p=array([0., 0., 0.]), s=1.0, ax_s=1, strict_check=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot basis of a rotation matrix.
- Parameters:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- Rarray-like, shape (3, 3), optional (default: I)
Rotation matrix, each column contains a basis vector
- parray-like, shape (3,), optional (default: [0, 0, 0])
Offset from the origin
- sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the frame that will be drawn
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- strict_checkbool, optional (default: True)
Raise a ValueError if the rotation matrix is not numerically close enough to a real rotation matrix. Otherwise we print a warning.
- kwargsdict, optional (default: {})
Additional arguments for the plotting functions, e.g. alpha
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
Examples using pytransform3d.rotations.plot_basis#
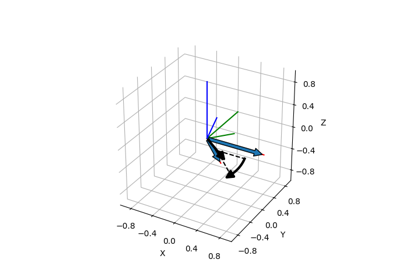
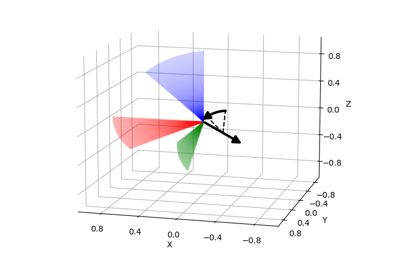
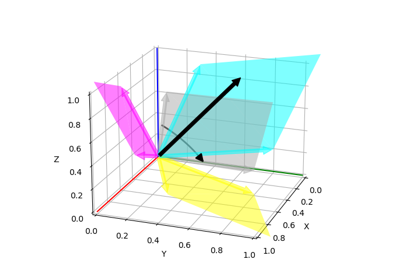
Axis-Angle Representation from Two Direction Vectors
Axis-Angle Representation from Two Direction Vectors
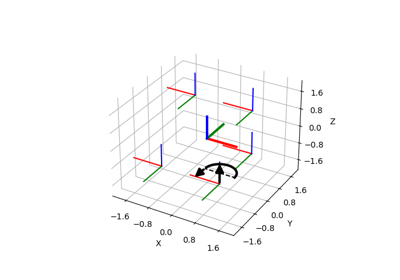
Convention for Rotation: Passive / Active, Extrinsic / Intrinsic
Convention for Rotation: Passive / Active, Extrinsic / Intrinsic