pytransform3d.transform_manager.TransformManager#
- class pytransform3d.transform_manager.TransformManager(strict_check=True, check=True)[source]#
Bases:
TransformGraphBaseManage transformations between frames.
This is a simplified version of ROS tf [1] that ignores the temporal aspect. A user can register transformations. The shortest path between all frames will be computed internally which enables us to provide transforms for any connected frames.
Suppose we know the transformations A2B, D2C, and B2C. The transform manager can compute any transformation between the frames A, B, C and D. For example, you can request the transformation that represents frame D in frame A. The transformation manager will automatically concatenate the transformations D2C, C2B, and B2A, where C2B and B2A are obtained by inverting B2C and A2B respectively.
Warning
It is possible to introduce inconsistencies in the transformation manager. Adding A2B and B2A with inconsistent values will result in an invalid state because inconsistencies will not be checked. It seems to be trivial in this simple case but can be computationally complex for large graphs. You can check the consistency explicitly with
TransformManager.check_consistency().The TransformManager does not directly support serialization because we don’t want to decide for a specific format. However, it allows conversion to a dict with only primitive types that is serializable, for instance, as JSON. If a more compact format is required, binary formats like msgpack can be used. Use
TransformManager.to_dict()andTransformManager.from_dict()for this purpose.- Parameters:
- strict_checkbool, optional (default: True)
Raise a ValueError if the transformation matrix is not numerically close enough to a real transformation matrix. Otherwise we print a warning.
- checkbool, optional (default: True)
Check if transformation matrices are valid and requested nodes exist, which might significantly slow down some operations.
References
[1]Foote, T. (2013). tf: The transform library. In IEEE Conference on Technologies for Practical Robot Applications (TePRA), Woburn, MA, USA, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/TePRA.2013.6556373.
Methods
__init__([strict_check, check])add_transform(from_frame, to_frame, A2B)Register a transformation.
Check consistency of the known transformations.
Get number of connected components.
from_dict(tm_dict)Create transform manager from dict.
get_transform(from_frame, to_frame)Request a transformation.
has_frame(frame)Check if frame has been registered.
plot_connections_in(frame[, ax, ax_s, whitelist])Plot direct frame connections in a given reference frame.
plot_frames_in(frame[, ax, s, ax_s, ...])Plot all frames in a given reference frame.
remove_frame(frame)Remove a frame (node) from the graph.
remove_transform(from_frame, to_frame)Remove a transformation.
set_transform_manager_state(tm_dict)Set state of transform manager from dict.
to_dict()Convert the transform manager to a dict that is serializable.
write_png(filename[, prog])Create PNG from dot graph of the transformations.
Attributes
Rigid transformations between nodes.
- property transforms#
Rigid transformations between nodes.
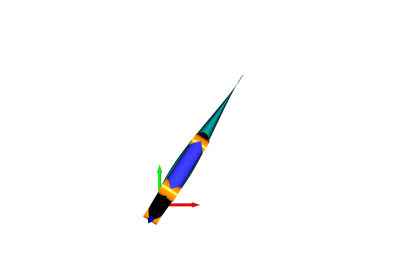
- plot_frames_in(frame, ax=None, s=1.0, ax_s=1, show_name=True, whitelist=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot all frames in a given reference frame.
Note that frames that cannot be connected to the reference frame are omitted.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Reference frame
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the frame that will be drawn
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- show_namebool, optional (default: True)
Print node names
- whitelistlist, optional (default: None)
Frames that must be plotted
- kwargsdict, optional (default: {})
Additional arguments for the plotting functions, e.g. alpha
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
- Raises:
- KeyError
If the frame is unknown
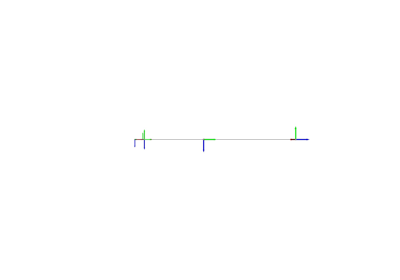
- plot_connections_in(frame, ax=None, ax_s=1, whitelist=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot direct frame connections in a given reference frame.
A line between each pair of frames for which a direct transformation is known will be plotted. Direct means that either A2B or B2A has been added to the transformation manager.
Note that frames that cannot be connected to the reference frame are omitted.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Reference frame
- axMatplotlib 3d axis, optional (default: None)
If the axis is None, a new 3d axis will be created
- ax_sfloat, optional (default: 1)
Scaling of the new matplotlib 3d axis
- whitelistlist, optional (default: None)
Both frames of a connection must be in the whitelist to plot the connection
- kwargsdict, optional (default: {})
Additional arguments for the plotting functions, e.g. alpha
- Returns:
- axMatplotlib 3d axis
New or old axis
- Raises:
- KeyError
If the frame is unknown
- write_png(filename, prog=None)[source]#
Create PNG from dot graph of the transformations.
Warning
Note that this method requires the Python package pydot and an existing installation of graphviz on your system.
- Parameters:
- filenamestr
Name of the output file. Should end with ‘.png’.
- progstr, optional (default: dot)
Name of GraphViz executable that can be found in the $PATH or absolute path to GraphViz executable. Possible options are, for example, ‘dot’, ‘twopi’, ‘neato’, ‘circo’, ‘fdp’, ‘sfdp’.
- Raises:
- ImportError
If pydot is not available
- to_dict()[source]#
Convert the transform manager to a dict that is serializable.
- Returns:
- tm_dictdict
Serializable dict.
- static from_dict(tm_dict)[source]#
Create transform manager from dict.
- Parameters:
- tm_dictdict
Serializable dict.
- Returns:
- tmTransformManager
Deserialized transform manager.
- set_transform_manager_state(tm_dict)[source]#
Set state of transform manager from dict.
- Parameters:
- tm_dictdict
Serializable dict.
- add_transform(from_frame, to_frame, A2B)#
Register a transformation.
- Parameters:
- from_frameHashable
Name of the frame for which the transformation is added in the to_frame coordinate system
- to_frameHashable
Name of the frame in which the transformation is defined
- A2BAny
Transformation from ‘from_frame’ to ‘to_frame’
- Returns:
- selfTransformManager
This object for chaining
- check_consistency()#
Check consistency of the known transformations.
The computational cost of this operation is very high.
- Returns:
- consistentbool
Is the graph consistent, i.e., if there are two ways of computing A2B, do they give almost identical results?
- connected_components()#
Get number of connected components.
If the number is larger than 1 there will be frames without connections.
- Returns:
- n_connected_componentsint
Number of connected components.
- get_transform(from_frame, to_frame)#
Request a transformation.
- Parameters:
- from_frameHashable
Name of the frame for which the transformation is requested in the to_frame coordinate system
- to_frameHashable
Name of the frame in which the transformation is defined
- Returns:
- A2BAny
Transformation from ‘from_frame’ to ‘to_frame’
- Raises:
- KeyError
If one of the frames is unknown or there is no connection between them
- has_frame(frame)#
Check if frame has been registered.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
Frame name
- Returns:
- has_framebool
Frame is registered
- remove_frame(frame)#
Remove a frame (node) from the graph.
- Parameters:
- frameHashable
The frame to remove.
- Returns:
- selfTransformManager
This object for chaining.
- remove_transform(from_frame, to_frame)#
Remove a transformation.
Nothing happens if there is no such transformation.
- Parameters:
- from_frameHashable
Name of the frame for which the transformation is added in the to_frame coordinate system
- to_frameHashable
Name of the frame in which the transformation is defined
- Returns:
- selfTransformManager
This object for chaining